In upcoming articles I will be deep diving into the multidimensional factors which will contribute to achieving sustainable zero carbon city transport. We will look at living labs in multimodal transport which represent a dynamic and innovative approach to developing, testing, and implementing sustainable mobility solutions within real-world urban and regional environments. These environments serve as experimental ecosystems where stakeholders—including governments, industry, academia, and citizens—collaborate to foster digitalization, integration, and social innovation aimed at transforming transportation systems into more efficient, resilient, and user-centric networks. Here is a brief synopsis of some upcoming content.

Introduction
Urban environments worldwide face increasing challenges related to sustainability, congestion, pollution, and climate change. To address these issues, the integration of innovative technologies such as micro mobility solutions, Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and real-time modeling for modal shift strategies is vital. This report explores how these tools contribute to sustainable urban transformation, emphasizing micro mobility as a key component, supported by VR/AR environments and sophisticated modeling techniques.
1. Visualizing Urban Sustainability Transition
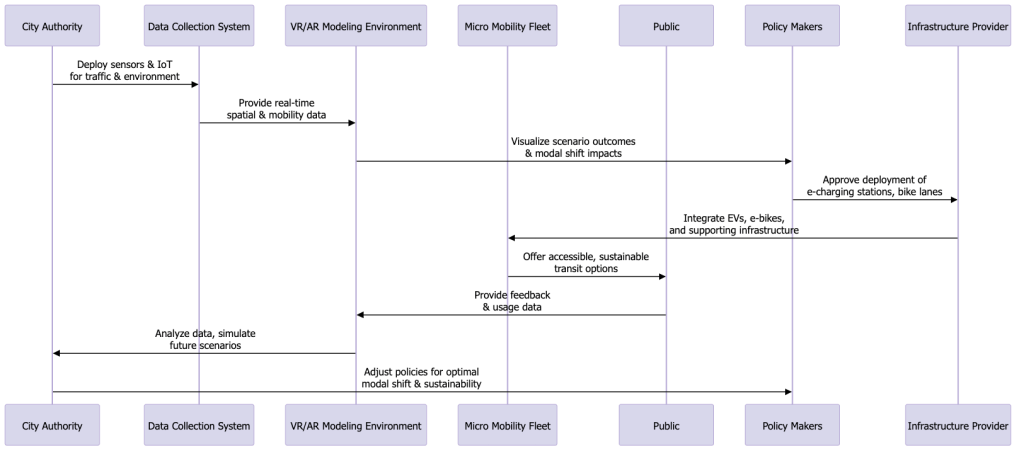
Understanding the complex interactions in urban sustainability requires detailed process mapping. Below is a mermaid sequence chart illustrating the typical flow of a micro mobility-enabled urban sustainability transition leveraging VR/AR modeling, real-time data, and modal shift strategies.
2. Key Concepts and Entities
| Concept/Entity | Description | Significance in Urban Sustainability & Micro Mobility |
|---|---|---|
| Micro Mobility | Small, electric, shared or private vehicles (e-bikes, e-scooters, small EVs) for short-distance travel | Reduces congestion, emissions, and enhances urban accessibility |
| VR/AR Modeling Environment | Virtual/augmented simulations of urban mobility and infrastructure | Enables scenario testing, stakeholder engagement, and planning accuracy |
| Modal Shift | Transition from private car use to sustainable modes (public transit, cycling, micro mobility) | Key to reducing GHGs, pollution, and traffic congestion |
| Real-time Data & IoT | Sensors, connected devices providing live traffic, environmental, and usage data | Facilitates dynamic management, optimization, and predictive planning |
| Sustainability Transition | Shift towards low-carbon, resource-efficient urban systems | Drives policy innovation, infrastructure adaptation, and behavioral change |
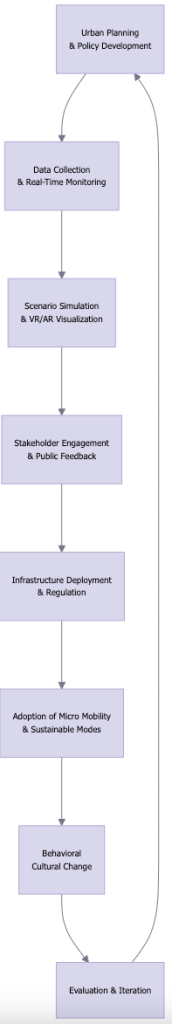
3. Processes Driving Modal Shift with Micro Mobility
4. Key Factors for Success and Challenges
| Factors | Details | Impact on Sustainability Transition |
|---|---|---|
| Technological Innovation | Advanced EVs, IoT, AR/VR tools | Enables realistic planning and rapid deployment |
| Policy & Regulation | Supportive policies for EV, micro mobility | Facilitates adoption & infrastructure development |
| Public Engagement | VR/AR experiences for awareness | Fosters behavioral change & acceptance |
| Infrastructure | Charging stations, bike lanes | Critical for safe, accessible mobility |
| Data Management | Real-time analytics, privacy concerns | Optimizes operations but raises privacy challenges |
| Behavioral Barriers | Resistance to change, safety concerns | Requires education and incentives |
5. Impacts of Micro Mobility & Modal Shift
Environmental
| Impact | Description | Supporting Extracts |
|---|---|---|
| Reduction in GHG Emissions | EV micro mobility lowers urban carbon footprint | [ 1 , 3 , 8 , 55 ] |
| Decreased Air Pollution | Cleaner air through modal shift | [ 10 , 222 , 236 ] |
| Less Traffic Congestion | Reduced private car use | [ 518 , 530 ] |
Socio-economic
| Impact | Description | Supporting Extracts |
|---|---|---|
| Improved Accessibility | Equitable mobility options | [ 147 , 552 ] |
| Job Creation | EV manufacturing, infrastructure, services | [ 515 , 575 ] |
| Public Health Benefits | Less pollution, active lifestyles | [ 494 , 589 ] |
Urban Development
| Impact | Description | Supporting Extracts |
|---|---|---|
| Sustainable Land Use | Promotes mixed-use, walkable cities | [ 65 , 299 ] |
| Smart Infrastructure | Integration of AR/VR in planning | [ 502 , 510 ] |
| Resilient Urban Systems | Adaptation to climate impacts | [ 352 , 388 ] |
6. Challenges & Opportunities
| Challenges | Opportunities |
|---|---|
| Cybersecurity & Data Privacy | Use of blockchain & secure IoT |
| High Initial Investment | Green bonds, public-private partnerships |
| Behavioral Resistance | VR/AR education campaigns |
| Infrastructure Gaps | Smart grid, scalable EV charging |
| Regulatory Barriers | Policy harmonization & incentives |
7. Opportunities in Technology & Policy
| Technology | Role & Impact | Supporting Extracts |
|---|---|---|
| AR/VR Visualization | Scenario testing, stakeholder engagement | [ 1 , 54 , 164 , 502 ] |
| IoT & Data Analytics | Real-time monitoring & adaptive management | [ 213 , 214 , 261 ] |
| Electric & Hybrid Vehicles | Decarbonizing urban mobility | [ 8 , 55 , 629 ] |
| AR-Enabled Infrastructure | Construction, maintenance, & public info | [ 608 , 618 ] |
| Smart Grids & Charging | Reliable EV infrastructure | [ 470 , 622 ] |
| Policy | Impact & Strategy | Supporting Extracts |
| ————– | ———————— | ————————- |
| Incentives & Subsidies | Accelerate adoption of EVs & micro mobility | [ 469 , 486 , 614 ] |
| Urban Planning & Zoning | Support multimodal infrastructure | [ 352 , 632 , 635 ] |
| Data Privacy & Security Regulations | Balance innovation & security | [ 261 , 502 ] |
| Sustainable Mobility Policies | Reduce GHG & traffic congestion | [ 518 , 605 , 632 ] |
| Public Engagement & Education | Foster behavioral change | [ 147 , 164 , 269 ] |
8. Impact Assessment & Future Directions
Quantitative Impacts
- Emission Reductions: Potential to lower urban CO2 by up to 65% via modal shift [ 55 ]
- Traffic Decongestion: Improved urban flow, reducing commute times by 20-30% [ 518 ]
- Job Creation: Micro mobility and EV infrastructure could generate 10+ million jobs globally [ 515 , 615 ]
Qualitative Impacts
- Enhanced urban resilience & climate adaptation
- Increased community participation & environmental awareness
- Digital twin & VR environments for ongoing planning & public engagement
9. Conclusion
The transition toward sustainable urban mobility harnessing micro mobility, VR/AR modeling, and modal shift strategies offers significant potential for environmental, social, and economic benefits. Success hinges on technological innovation, supportive policies, stakeholder engagement, and robust data management. Embracing these integrated tools will facilitate smarter, greener, and more inclusive cities capable of meeting climate goals and improving urban life quality.
This comprehensive approach created in Corpora.ai , supported by recent extracts and data, illustrates a clear pathway for cities to achieve sustainable mobility through cutting-edge technologies and participatory planning.